Climate Crisis in 2024: Unprecedented Temperatures and Impacts
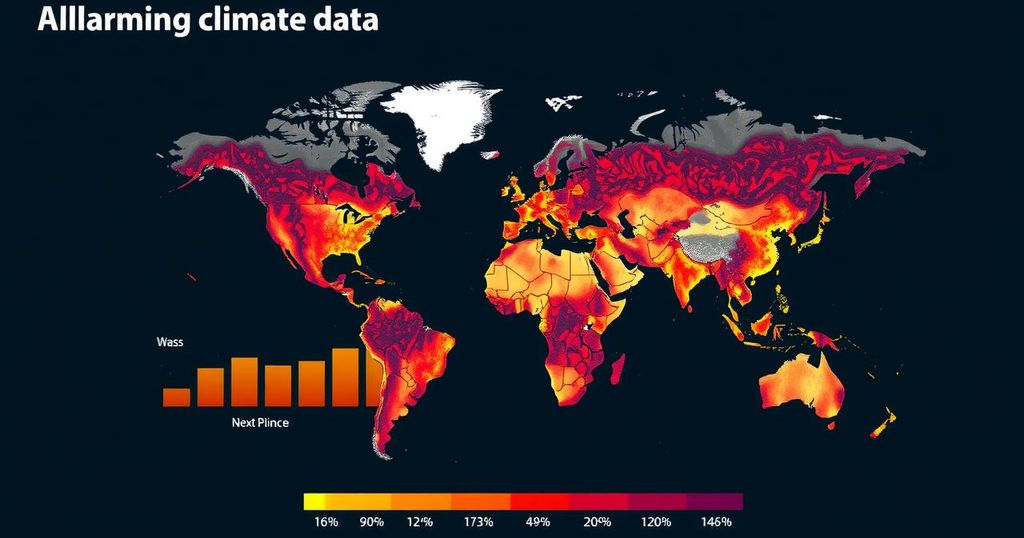
As of 2024, the world faces unprecedented climate challenges, with global temperatures reaching alarming levels, extreme weather such as heatwaves and droughts, and continued emissions of greenhouse gases. While renewable energy development shows promise, emissions are still on the rise, demanding urgent global action to mitigate the climate crisis and its impacts.
The climate crisis continues to escalate, as evidenced by alarming new records set in 2024. The United Nations Secretary-General, António Guterres, aptly stated last year, “The era of global boiling has arrived,” a sentiment he has reiterated as 2024 threatens to become the hottest year on record. Global temperatures have risen significantly, reaching 1.62°C higher than the 1850-1900 average, and it is projected that this year may be the first to surpass the critical 1.5°C increase compared to preindustrial levels. Southern Europe, in particular, has experienced extreme heat, with reports indicating that certain regions faced unprecedented heat stress days. The Copernicus Climate Change Service highlighted that parts of Greece and western Turkey endured extreme heat conditions for over two months, presenting serious challenges for vulnerable populations, including migrant workers and detainees, who often lack adequate cooling measures. Additionally, the oceans are not spared, as marine heatwaves reached alarming levels, surpassing those of the previous year. These seawater temperature increases have intensified rainfall patterns, contributing to destructive hurricanes and anomalous precipitation events globally. Data from the Lancet indicates that a staggering 61% of global land experienced increased extreme rainfall from 1994 to 2023. Conversely, regions dependent on consistent freshwater sources experienced devastating droughts. The Amazon rainforest has been significantly affected, illustrating the divide as nearly half of the planet’s land area endured drought conditions for at least one month this year. Despite the widespread recognition of climate issues, emissions of greenhouse gases continue unabated. Carbon dioxide levels have surged to 420 parts per million, reflecting a 51% increase since preindustrial times. Methane and nitrous oxide have also seen substantial rises, demonstrating humanity’s ongoing reliance on fossil fuels. Unfortunately, projections show that global emissions will rise by 0.8% by the end of 2024. The effects of climate change are increasingly evident, as rising sea levels threaten to submerge coastal cities across the globe. Although the land ice is melting and contributing to sea level rise, the synergistic feedback loop between temperature increases and sea ice reduction accelerates the heating process. Predictions indicate that even controlling temperature rise to 2°C could see one in five people living in areas at risk of being underwater. Nonetheless, there is a glimmer of hope as the renewable energy sector is expanding rapidly. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) reported a record total capacity of 3,870 GW globally in 2023, a significant leap mainly driven by efforts in nations like China. However, developing countries are lagging behind, showing only marginal increases in comparison. Additionally, electric vehicle registrations are on the rise, signifying progress in the shift towards greener technology, though this growth is unevenly distributed globally. In summary, while there are crucial advancements in renewable energy, the stark reality of climate change and its associated impacts remain daunting. 2024 serves as a critical reminder of the urgent need for coordinated global action to combat climate change effectively.
The climate crisis has reached an alarming stage, with 2024 set to become potentially the hottest year recorded in history. The increasing global temperatures and the dire implications for weather patterns, ocean temperatures, and greenhouse gas emissions are clear indicators of the severe impact humanity’s reliance on fossil fuels has on the planet. Extreme weather events, including heatwaves, heavy rainfall, and droughts, are becoming more commonplace, highlighting the urgent need for immediate action and a transition to renewable energy sources to mitigate these effects. As nations strive to meet net-zero emissions goals, there is hope in the growth of renewable energy technologies amidst the continuing challenge of rising temperatures and sea levels affecting global populations.
In conclusion, the data and trends observed in 2024 underscore the severe and urgent nature of the climate crisis. The increase in global temperatures has direct consequences on both weather patterns and ocean conditions, leading to extreme weather events and significant challenges for vulnerable communities. Despite promising advancements in renewable energy and electric vehicle adoption, the continued rise in greenhouse gas emissions poses a significant threat to our environment and future. Coordinated global action and resource mobilization remain essential to addressing the climate crisis effectively and ensuring a sustainable future for generations to come.
Original Source: www.theguardian.com







