Understanding the DANA: A Storm System of Catastrophic Potential in Spain
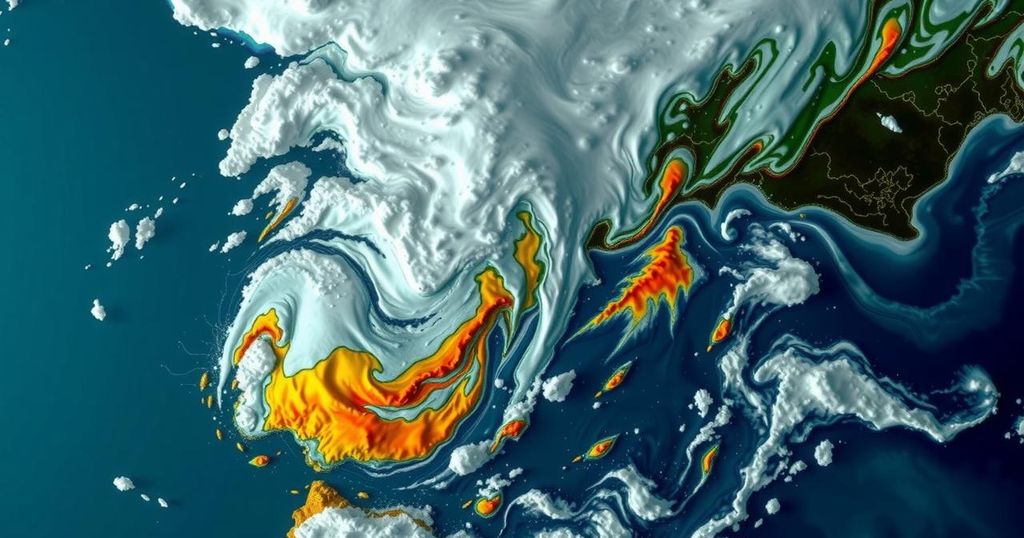
Eastern Spain has recently experienced devastating flooding due to a storm system known as a DANA, characterized by isolated low-pressure areas causing extreme rainfall. An area like Chiva recorded over 19 inches of rain within hours, leading to significant flooding and storm damage associated with the storm’s characteristics, which include lightning, hail, and tornadoes. DANAs typically occur during warmer months, exacerbating risks when coupled with the region’s mountainous terrain.
The recent flooding in eastern Spain has been attributed to a severe weather phenomenon known as a “DANA,” an acronym for “Depresión Aislada en Niveles Altos,” which translates as an isolated low-pressure system at upper levels. A DANA occurs when a low-pressure area becomes detached from the jet stream’s guidance. These storms are characterized by an interaction with the warm waters of the Mediterranean Sea, which results in significant evaporation and a subsequent unstable atmosphere conducive to the development of storms. This particular DANA has unleashed torrential rain leading to catastrophic flooding. Residents in regions such as Chiva, west of Valencia, witnessed an astounding 19.33 inches of rain within just eight hours, with 13.55 inches falling in a mere four hours and an extreme 6.5 inches in one hour. Such climatic conditions mirror those observed during Hurricane Helene, although each storm’s meteorological characteristics differ. DANA storms can generate severe lightning, substantial hail, and even tornadoes, as was noted in reports from eastern Spain. If a DANA directs easterly winds along the coastal areas, it can force moisture-laden air masses into the mountainous terrain, particularly around Valencia. This orographic lift results in pronounced rainfall totals, exacerbating the flooding risk. While DANAs typically occur throughout the summer and fall due to warm sea waters, the current storm has reached unprecedented levels of severity, resulting in significant damage and loss of life.
The DANA storm phenomenon has become increasingly relevant as it impacts southern and eastern Spain annually, particularly during the warmer months when sea temperatures rise. This isolated low-pressure system often leads to catastrophic weather, as evidenced by the recent flooding incidents that have created widespread damage and raised concerns regarding climate change and its effect on storm frequency and intensity. Due to the Mediterranean Sea’s influence and its topographical relationship with nearby mountains, southwestern Europe faces unique meteorological challenges, particularly in terms of heavy precipitation and associated flooding risks. Understanding the mechanics of DANA systems is crucial for improving forecast accuracy and disaster preparedness.
In summary, the DANA storm affecting eastern Spain has demonstrated the potential for severe weather phenomena to cause historic flooding, particularly in regions with significant elevation changes. The interaction of warm Mediterranean waters with an isolated low-pressure system has resulted in catastrophic rainfall, highlighting the importance of meteorological knowledge in predicting such events. Enhanced awareness and understanding of these systems may aid in future mitigation efforts against similar natural disasters.
Original Source: www.foxweather.com







